|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|

The placenta is a unique organ, the “lifeline” between mother and child, playing a critical role in fetal development and maternal health. Besides its biological functions, it holds immense potential for medical research, regenerative medicine, and disease prevention. For research scholars and medical professionals, the placenta serves as a gateway to discoveries that can enhance maternal and neonatal health worldwide.
The Placenta’s Role in Maternal Health and Development
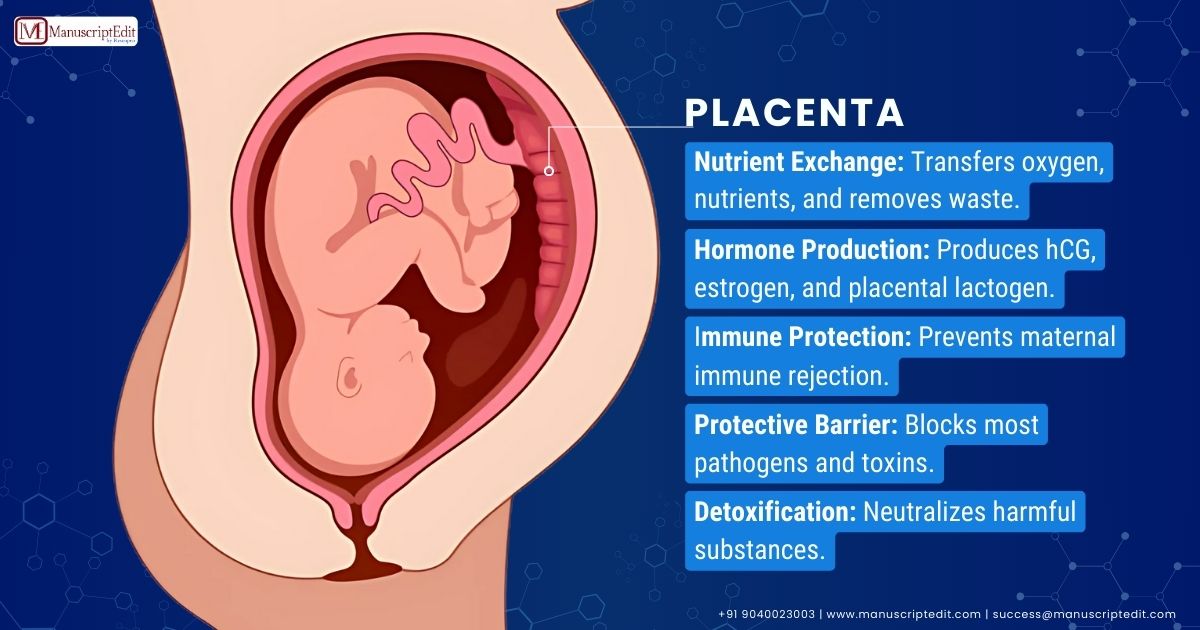
The placenta plays a critical role in healthy pregnancy outcomes:
- Nutrient Exchange: Mediates the transport of glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids, removing waste products including carbon dioxide.
- Hormone Production: Produces essential hormones like hCG, progesterone, and estrogen, which regulate fetal development.
- Immune Protection: Transfers maternal antibodies to the fetus, providing early immunity.
- Toxin Filtration: A Nature Medicine (2023) study revealed that the placenta blocks over 50% of harmful toxins, underscoring its protective role.
However, severe complications like placental dysfunction can cause preeclampsia and preterm births. The Lancet (2021) reports that placental insufficiency contributes to up to 15 million preterm births annually, emphasizing the urgent need for innovative research and solutions.
Need help writing your manuscript on maternal health or placental disorders? We can help you meet journal guidelines with precision and clarity.
Research Advances in Placental Health
Placental health research is essential for addressing complications that impact 10-15% of pregnancies worldwide. Major findings include:
- Preeclampsia: Affects 5-8% of pregnancies and is associated with high maternal mortality rates.
- Gestational Diabetes: Impacts 2-10% of pregnancies, increasing neonatal and long-term health risks.
- Placental Insufficiency: Occurs in 6-8% of pregnancies, leading to low birth weight and neonatal complications.
A 2023 American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology study showed that early diagnosis and timely interventions can reduce preterm births by up to 40%.
Technological Innovations in Placental Science
Recent advancements in imaging, organoids, and genomics have revolutionized placental research:
- Imaging Technologies: 3D and Doppler ultrasounds provide detailed insights into blood flow.
- Placental Organoids: These models simulate placental function, enabling studies on drug and toxin effects (Cell Stem Cell, 2023).
- Genomics and Biomarkers: Early detection of preeclampsia and placental disorders is now possible through predictive biomarkers (Journal of Genomics, 2023).
- Regenerative Medicine: Placental mesenchymal stem cells (PMSCs) show promise in repairing damaged tissues and treating autoimmune diseases like arthritis (Nature, 2023).
These innovations showcase the placentaŌĆÖs transformative potential for maternal-fetal medicine.
Let Manuscriptedit help turn your groundbreaking findings into polished, high-impact publications. Our experts specialize in delivering research ready for leading journals. Is your work addressing innovative research in reproductive health or maternal-fetal medicine? At Manuscriptedit, we provide customized research support, including medical writing, statistical analysis, and publication support, to help you reach high-impact journals.
Common Research Areas Involving the Placenta
The diverse roles of the placenta make it an interesting area to research within many medical disciplines. New avenues have recently been opened, mainly as developments in genomics, immunology, and stem cell technologies have made it possible. Some of the new emphases are as follows:
1. Placental Pathology and Pregnancy Complications:
Most pregnancy complications are associated with disorders of placental function, including preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). Biomarkers and underlying molecular mechanisms that lead to placental dysfunction are now being identified to enhance early detection and intervention in pregnancy. Research studies on these complications have focused on oxidative stress, inflammatory processes, and immune system dysregulation.
2. Placental Stem Cells and Regenerative Medicine:
Perhaps the most captivating application of placental research is using stem cells taken from placentas for regenerative medicine. Amniotic membranes and umbilical cord-derived stem cells could differentiate into all cell types and be applied to diseases such as heart disease, neurodegenerative conditions, and autoimmune disorders. The placenta might hold vast potential for regenerative therapeutics that can be extracted in a manner much more accessible than stem cells from other sources.
3. Placental Microbiome:
New research has shown that the placenta has a distinguishable microbiome, a constellation of microorganisms that influence maternal and fetal health. The study of the placental microbiome composition and functionality may reveal new information concerning prenatal development, immune system programming, and the origins of diseases such as asthma, obesity, and allergies. The study of the role of the microbiome in pregnancy lies at an exciting frontier for medicine.
4. Placenta as Model of Study on Disease:
The trophoblast cells in the placenta invade and remodel the uterine wall to establish pregnancy, similar to cancer cells invading surrounding tissues. The study of Trophoblast behaviour and placental invasion has highlighted the mechanism of metastasis behind cancer. These studies, in the context of the biology of the placenta, are taken to find new therapeutic strategies for cancer.
5. Function of Placenta in Different Populations:
Placental function varies significantly between different populations based on race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and other factors related to pregnancy outcomes. Thus, it has been necessary to investigate how these differences have contributed to disparities in maternal-fetal health, including higher risks of preterm birth and low birth weight in certain groups of women. Understanding how placental function varies between populations is important in the development of personalized medical interventions in pregnancy care.
Conclusion: The Importance of Placenta in Medical Science
It is indeed one of human biology’s most vital and least-appreciated organs. It executes multifaceted roles, ranging from nutrient delivery to immune system modulates, pivotal to the success of pregnancy and fetal development. The placenta has emerged as a central research subject in many medical sciences, focusing on pregnancy complications and regenerative medicine.
With the burgeoning knowledge of placental biology, the organ has tremendous potential for improvements in prenatal care and treatments for various diseases. The opportunities of the placenta include stem cell differentiation, immune system modulation, and involvement in chronic diseases. Such factors find it at the centre stage of medical research today.
The placenta presents a gateway to further and groundbreaking research for researchers and scholars in the field, promising changes in maternal and fetal healthcare. The placenta is not a temporary organ; it’s dynamic and indispensable for human health.
Extra Insights: The Placenta’s Impact Beyond Pregnancy
While the placenta serves its primary role in pregnancies, its importance is now expanding with medical research. Just a few more points at which it has far-reaching results include:
1. Long term health effects
Placental health impacts the long-term outcome of both the mother and the child. Conditions such as preeclampsia and placental insufficiency increase the future risk of cardiovascular disease in the mother and metabolic disorders in the offspring, so early detection and treatment are essential.
2. Regenerative Medicine Potential
Placental-derived stem cells from amniotic membranes and umbilical cords may be used soon to regenerate damaged body parts. These stem cells have already shown promise in treating heart disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune diseases. Such therapies may eventually become a reality.
3. Personalized Medicine
Understanding placental function variations among individuals can lead to personalized healthcare for pregnant women. Factors such as genetics, environment, and maternal health affect placental performance, and tailoring care based on this can improve outcomes for both mother and baby.
4. Epigenetics and Disease Programming
The placenta is involved in epigenetic programming: through diet, stress, and other means of environmental exposure, gene expression in both the placenta and the fetus can be influenced. The activities occurring early in life impact later health, so learning to break this link can aid in preventing disease in later life.
The Medical Significance of the Placenta
The placenta’s influence transcends pregnancy, influencing future health outcomes of both mother and child. Advances in research may lead to improved regenerative medicine, customized care, and disease prevention and make it a central focus in modern medical studies.
Prenatal development research is not only scientifically intriguing but also critically important for improving healthcare outcomes. This field demands meticulous exploration, and publishing your findings in reputed journals ensures your work reaches the global academic community. ManuscriptEdit is here to support you at every step of your publication journey. LetŌĆÖs work together to enhance your research impact
The Economic and Clinical Impact of Placental Dysfunction
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that complications from placental insufficiency contribute to $20 billion in annual healthcare costs. Early detection and proper monitoring could prevent up to 20% of preterm births (NIH, 2022), significantly improving outcomes for mothers and newborns.
These economic and clinical findings underline the importance of continued research.
Whether youŌĆÖre conducting systematic reviews, meta-analyses, or clinical studies, our team ensures your work meets the highest standards for Q1 and Q2 journals. Let us support your success.
Case Study Highlights: Translating Placental Science into Practice
- Early Diagnosis Tools: Researchers at the University of Oxford identified placental proteins that predict preeclampsia months before symptoms appear.
- Regenerative Therapies: Placental-derived tissues are showing promise in treating chronic conditions and restoring organ function.
- Targeted Interventions: Genetic and imaging technologies allow precise management of high-risk pregnancies.
These examples highlight how advances in placental science can transform maternal and neonatal health outcomes.
Partner with Manuscriptedit for Research Success
Placental research is driving innovations in maternal health, offering solutions to complications that affect millions globally. Whether youŌĆÖre a researcher or medical professional, your work can shape clinical practice, advance healthcare, and improve outcomes worldwide.
Your research deserves a global platform. Partner with Manuscriptedit today and let us help you publish in prestigious journals like Nature and Springer.
Let Your Research Soar with Manuscriptedit
The future of maternal and fetal health relies on innovative research like yours. DonŌĆÖt let language, formatting, or editorial challenges hold you back. Manuscriptedit is here to ensure your work shines and reaches a global audience.
Contact us today to get started!
¤īÉhttps://lnkd.in/fbaE3tv
¤ō×+91-904-002-3003 (IN)
References
- Nature Medicine, Placental Function and Development, 2022.
- International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, Complications Linked to Placental Insufficiency, 2021.
- The Lancet, Placental MRI in Pregnancy: A New Diagnostic Tool, 2020.
- Science Translational Medicine, Genetic Loci Linked to Preeclampsia, 2021.
- The Journal of Clinical Investigation, Biomarkers for Gestational Diabetes, 2022.
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, Innovations in Placental Research, 2023.
- World Health Organization, Global Economic Impact of Maternal Complications, 2023.



