|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
 Citation databases such as Scopus provide research impact metrics citation analysis—indicators vital to academia and the scientific community. The leading abstract and citation database, Scopus, offers thorough coverage of the world’s research output, making precise tracking and analysis of citations possible.
Citation databases such as Scopus provide research impact metrics citation analysis—indicators vital to academia and the scientific community. The leading abstract and citation database, Scopus, offers thorough coverage of the world’s research output, making precise tracking and analysis of citations possible.
This makes evaluating research quality, influence, and impact easier, which helps inform choices about funding, promotion, and policy.
What are the metrics for research impact?
Research impact measures measure how research impacts academia, business, and society. Citation counts, citation rates (such as the h-index), altmetrics (such as social media mentions), publishing output, cooperation indices, research quality rankings, citations for patents, policies, and societal effect assessments (such as downloads, views, and shares) are examples of standard metrics.
Features and Coverage of Scopus
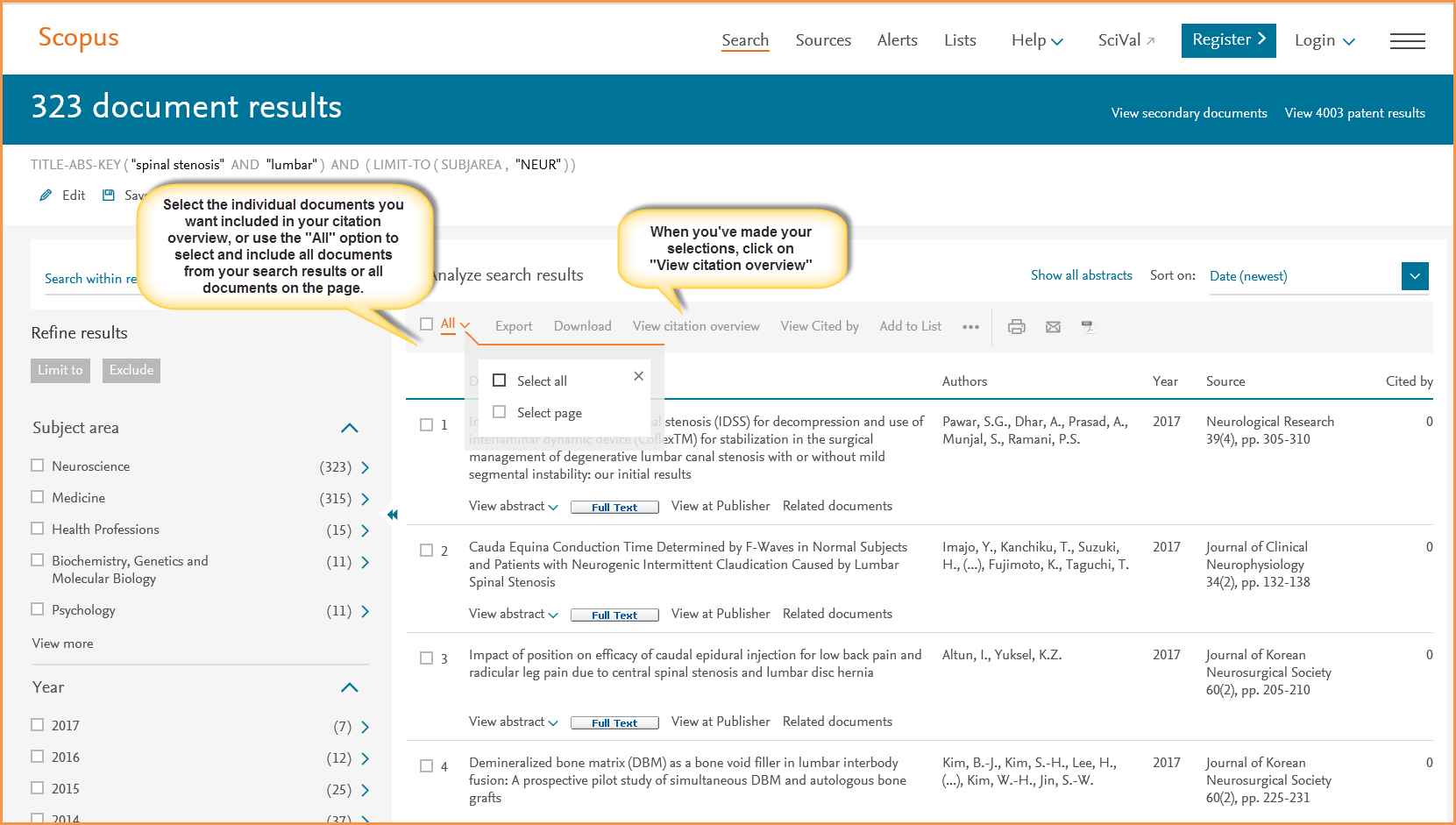
Scopus provides a comprehensive research landscape and offers a wide range of features and coverage, such as indexing conference proceedings, books, and patents; author and affiliation profiling with h-index and citation metrics; citation tracking and analysis tools; and advanced search features with filters by author, date, and document type.
What is the difference between citation impact and Impact Factor?
Citation impact quantifies the total number of citations a person or organization’s publications have received, indicating their reach and influence.
On the other hand, the Impact Factor (IF) is a journal-level metric that determines the average number of citations for each piece published in a journal. It serves as an indicator of the publication’s citation density and prestige.
The IF determines the average number of citations for each piece published in a journal. This journal-level metric indicates the citation density and prestige of the publication.
How do we measure the impact of research?
Evaluating the impact of research entails determining its influence and effects outside of academia.
Some metrics include cited counts, altmetrics, research quality rankings, patent citations, policy citations, cooperation indices, societal impact evaluations, and economic impact studies.
Benefits and Uses of Scopus
Through tracking citations and impact, assessing journals, identifying trends and possibilities, and promoting research discovery and evaluation, Scopus helps researchers, institutions, and funders.
It also allows for the analysis of research output, collaboration, and citation patterns to guide strategic choices, resource allocation, and evidence-based policymaking.
Comparison with Other Citation Databases
In contrast to Web of Science, Scopus includes conference proceedings, book chapters, and a more comprehensive range of journals. While Scopus provides more accurate citation tracking and sophisticated search capabilities than Google Scholar, it covers less non-peer-reviewed content overall.
Because every database has advantages, researchers frequently employ several databases to conduct thorough searches.
How to Use Scopus Effectively?
Use exact searching and filtering strategies, such as focusing on authors, dates, and keywords, to maximize Scopus—Configure notifications and alerts for fresh citations and publications.
Use Scopus’s analytics capabilities to guide funding decisions and research strategy. It may also generate citation reports, author biographies, and journal rankings for research evaluation and reporting.
Conclusion
To summarize, Scopus is an effective citation database that provides thorough coverage, sophisticated search tools, and useful metrics for assessing research. Its advantages include precise citation tracking, well-informed research techniques, and perceptive analytics.
References
- https://www.elsevier.com/products/scopus
- https://www.nihlibrary.nih.gov/training/introduction-scopus-2
- https://guides.lib.unc.edu/scopus



