To understand the rate of acceptance of scientific reports by researchers or scholars is often uncertain. When a manuscript is sent to the journal, questions start pouring in—the chances of acceptance, what sets one paper apart from another, and much more. These are mainly answered by an important metric: the acceptance rate. This article delves into the acceptance rate for Scientific Reports, compares it to other journals, and discusses how this could impact researchers.

What is the Acceptance Rate?
Acceptance rate refers to the percentage of submitted manuscripts accepted for publication in a journal. It is often considered an indicator of how competitive and selective a journal is. Generally, a higher acceptance rate signals less selectivity, while a lower rate suggests more stringent review and selectivity.
As an example, if the acceptance rate of a journal is 20%, then 20 manuscripts out of 100 submitted ones will be published. This number may not give a whole story about the quality of a journal, but it does provide an important clue regarding the level of competition and chances one might have to get published.

Therefore, the researcher’s knowledge of the journal’s acceptance rate is fundamental in framing his publication strategy, choosing where to submit his research, and how he can project the impact of his work once accepted.
Acceptance Rate of Scientific Reports
Scientific Reports is a fully open-access journal under the Nature Research brand, publishing various scientific disciplines such as biology, physics, chemistry, medical sciences, and environmental studies. As an open-access journal, it gives free access to its content, reaching maximum research dissemination to a global audience.
The acceptance rate for Scientific Reports is generally estimated to fall about 30% to 40%. This places it as moderately selective, balancing openness to new research and high standards of the peer review process. The acceptance rate could vary based on the quality of submissions in a specific period, the kind of research, or even the specific topical priorities of the journal’s editorial board.
Why is This Acceptance Rate Significant?
The acceptance rate of Scientific Reports is an essential metric for researchers and academic houses. With a rate between 30% and 40%, this journal appears selective yet not too restrictive. That is an essential fact that will interest researchers looking for a journal that can boast high standards yet possesses an attainable route to publication.
Scientific Reports is also a well-respected journal, particularly for essential and well-executed papers. Still, perhaps it is not of such importance or creativity to warrant publication in high-impact journals like Nature or Science. By providing open-access papers, Scientific Reports ensures research is accessible to a broader audience, thus increasing the more extensive dissemination and influence of once-published research.

How Does Scientific Reports Compare to Other Journals?
To better understand Scientific Reports’ position within the overall academic publishing landscape, comparing its acceptance rate against other reputable journals is helpful. The acceptance rates for different journals vary widely based on editorial standards, focus areas, and scientific community reputation.
Here are a few comparisons between major publishing companies:
1. Nature: Nature is among the most prestigious scientific journals, with an 8-10% acceptance rate. Known for publishing groundbreaking research, Nature has a highly selective peer-review process, accepting only high-impact papers with significant implications for their respective fields.
2. Science: Science is another top journal in the scientific community, with an acceptance rate of approximately 7-10%. Like Nature, it is very competitive, with a small percentage of research published from the ones it receives, often focusing on novel and transformative findings.
3. The Lancet: The acceptance rate of journals like The Lancet in medical research is around 5-7%. This means that it is one of the most exclusive in its field. The high standards reflect its global influence and commitment to publishing research that can lead to significant clinical advancement.
4. PLOS ONE: In the end, PLOS ONE, one of the open-access journals with the highest number of articles, has an acceptance rate between 60-70%. Though it publishes a wide variety of articles, the journal focuses more on scientific rigor than a novelty, thus making it possible to have a higher acceptance rate than journals such as Nature or Science.

Insights from These Comparisons-
Scientific Reports sits on a middle ground compared to such prestigious journals, accepting 30-40% of submitted papers. That indicates the journal keeps its peer-review process very strong while not at the level of highly exclusive journals like Nature or Science regarding the exclusion rate. A new study is presented in this excellent platform, for it has been made but not at a profound discovery that it will feature in A-tier journals.
On the other hand, the availability of scientific reports enables scientists to access extensive coverage of their research, which is ideal for those willing to publish their work across the globe. Its average acceptance rate reflects the imperative of keeping the scientific content with integrity and its pan-disciplinary scope.
Factors Affecting Acceptance Rate
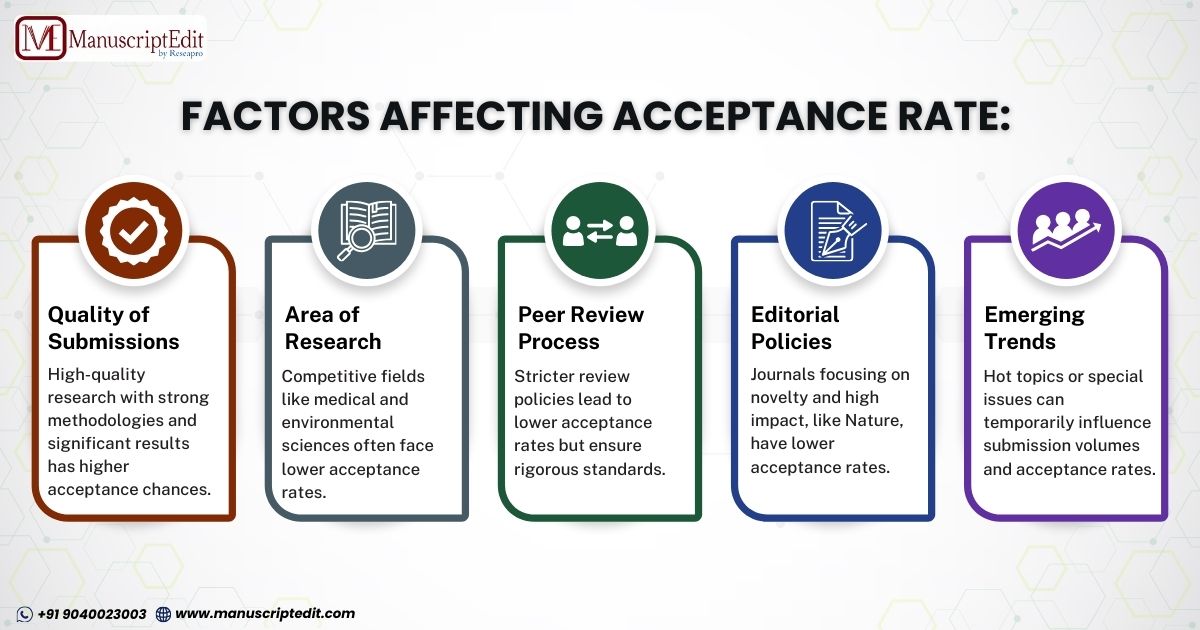
Several factors constitute a journal’s acceptance rate, and understanding these factors can guide researchers in their publishing strategy. Some of the most important influences are outlined below:
1. Quality of Submissions: The acceptance rate is affected mainly by the quality of research submitted to a journal. High-quality research with robust methodologies and precise, significant results are more likely to be accepted. Vice versa, a paper that lacks robust data or has methodological flaws is expected to be rejected.
2. Area of Research: Some research areas may be more prolific in terms of submissions to the journal than others, and this can skew the acceptance rate. Medical, biological, and environmental sciences often publish more heavily, and significant research is going on, which can thus lead to a lower acceptance rate in a journal. Specialized or niched areas might have fewer submissions, thus leading to a higher acceptance rate in the journal.
3. Peer Review Process: The peer-review process influences the acceptance rate. These journals that have stricter review processes tend to have lower acceptance rates. Scientific Reports is known for its fair and stringent peer review, thus upholding the integrity of the research that it publishes.
4. Editorial Policies: Editorial policies affect the acceptance rate. The journals focusing on novelty, impact, and high-quality data often have a lower acceptance rate. For instance, Nature accepts very few papers that are submitted to it. It is because this journal focuses solely on high-impact research. With a focus on high-quality but not transformative research, Scientific Reports can accept more papers.
5. Emerging Trends and Special Issues: Introducing particular issues or thematic volumes on emerging research trends can temporarily impact a journal’s acceptance rate. When a journal issues a call for papers on a hot topic, it might see a surge in submissions, which could positively or negatively affect the acceptance rate.

How the Acceptance Rate Affects Researchers?
For researchers, the acceptance rate of Scientific Reports is essential information about the publishing culture in the journal, the chance that the paper will have a fair chance of being published and its potential reach upon publication.
Here’s why the acceptance rate is essential:
1. Journal Selection according to the Strategic Plan: Knowing the acceptance rates will help a researcher choose a journal with which the scope, the quality of their results, and impact closely match. For example, if they come up with highly innovative results, then very exclusive journals with meagre acceptance rates might be their best bets. However, Scientific Reports is a well-balanced and respected outlet for solid studies of broad interest.
2. Improving Chances of Acceptance: Understanding what influences the acceptance rate allows researchers to improve the chances of accepting their papers. For instance, ensuring that research adheres to the journal’s focus areas, follows best practices in methodology, and is written can enhance the likelihood of acceptance, especially in competitive journals like Scientific Reports.
3. Impact and Visibility: Scientific Reports publication offers good visibility opportunities even with a moderate acceptance rate. Being an open-access journal, Scientific Reports makes sure to develop the visibility of research worldwide and increase its scope of academic impact. For most researchers, this journal strikes a balance between selectivity and accessibility.

Conclusion: Significance of acceptance rates for researchers
Acceptance rates are relatively high, about 30%-40%, and this should give a researcher access to such a well-respected publication line but in the middle of the scale in terms of exclusivity since top-level journals such as Nature or Science have much exclusive acceptance rates. This journal acceptance rate will help researchers decide where to place their work, ensuring they find the right fit for their research. The bottom line is that while acceptance rate is an important metric, quality, and relevance to your work remain the most crucial factors in any publication process.



