|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|

It is amazing that over 2.5 million academic papers are published each year, as per STM Report (2021). Still, most of them are rejected for some reasons such as errors or bias and even unethical practices. The very important process of peer review of academic publishing has been heavily criticized for its ineffectiveness and being merely based on opinion (Nature, 2020). These challenges make it harder to share important research and also make us doubt the academic publishing world.
From plagiarism detection to the appropriate reviewer selection, AI is transforming every aspect of peer review. For instance, according to a 2020 Springer Nature report, AI saves 70% time taken to select a reviewer. In this blog, statistical insights and real-life applications provide evidence on how AI is changing the academic publishing landscape. Discover the benefits of AI tools, the impact they are creating in reducing bias, and what remains in the field as it continues to expand.
The Challenges of Traditional Peer Review
Despite its importance, the peer review process is fraught with challenges:
- High Rejection Rates
Academic publishing suffers greatly from higher rejection rates. According to the STM Report (2021), for instance, only 10-20% of the submissions presented to high-impact journals are accepted. Most are rejected because of avoidable reasons like improper formatting or unclear methodologies among others in addition to being poorly proofread.
- Biases and Subjectivity
Another big problem is bias in peer review. According to studies, a significant 15% of the peer reviews conducted have been biased owing to personal or institutional bias (American Society for Microbiology, 2018). This compromises the integrity of the process and thus leads to unjust rejections or endorsements.
- Reviewer fatigue
Each year, over 2.5 million papers are submitted, resulting in reviewers often facing substantial workloads. A survey carried out by Wiley in 2019 revealed that 60% of reviewers feel overwhelmed, a situation that can compromise the quality of their evaluations and delay the publication process.
- Plagiarism and Ethical Violation
Detection of plagiarism is a formidable task requiring significant time to do. CrossRef (2021) reported that approximately 8% of manuscripts submitted undergo plagiarism check; however, the traditional process of doing this has proved ineffective in many ways and can quickly miss detection.
These challenges necessitate innovation and change in the process; hence, AI qualifies as a promising candidate in reforming the peer-review process.
How AI is Transforming Peer Review
1. Plagiarism Detection
The key players in plagiarism detection include AI-powered platforms like iThenticate and CrossRef. Such tools utilize complex algorithms, checking manuscripts against a very long list of sources such as published works, preprints, and online content. According to a CrossRef study conducted in 2021, AI technologies are capable of detecting 95% of plagiarized material in one minute. Even publishing houses such as Elsevier and Wiley have made use of AI-enhanced plagiarism detection during submission. The third approach reduces the chance for ethical violations, thereby also sustaining the credibility of published work.
2. Choosing Reviewers Automatically
Manuscripts need appropriate reviewers for a fair and informed assessment. AI systems form their connection between manuscripts and appropriate reviewers on the basis of metadata, keywords, and the experience of the reviewers. Springer Nature research reported that AI can reduce the time taken to identify a reviewer by as much as 70% (Springer Nature, 2020). Elsevier’s Reviewer Finder decreased the errors generated in matching the reviewers by 85% (Elsevier, 2019). This automation accelerates the process of work and decreases the possibility of mistakes in the selection of reviewers.
3. AI-Enhanced Manuscript Feedback
AI tools such as Grammarly and ScholarOne provide authors with thorough feedback on grammar, structure, and clarity so that they can hone their work before submission. More advanced tools are able to detect inconsistencies in data or methodologies. Research conducted by PLOS ONE has indicated that manuscripts polished with AI tools have a 25% higher acceptance rate (PLOS ONE, 2020). Tools such as Scholarcy also summarize dense text sections so that reviewers and authors can focus on the crux of the manuscript.
4. Reducing Bias in Peer Review
Bias can be a result of numerous factors, like a reviewer’s belief or institutional affinity. AI eradicates this problem because submissions are anonymized, and scoring is objective. The American Society for Microbiology has demonstrated that AI-enhanced, double-anonymous reviews reduced the rejections associated with bias by 40% (ASM, 2018). AI-based algorithms make decisions about manuscripts purely based on their merit and disregard authors’ identities, affiliations, or any demographics. This leads to an almost level playing field in academia and promotes the most diverse contributions from underrepresented researchers.
Benefits of AI-Powered Peer Review
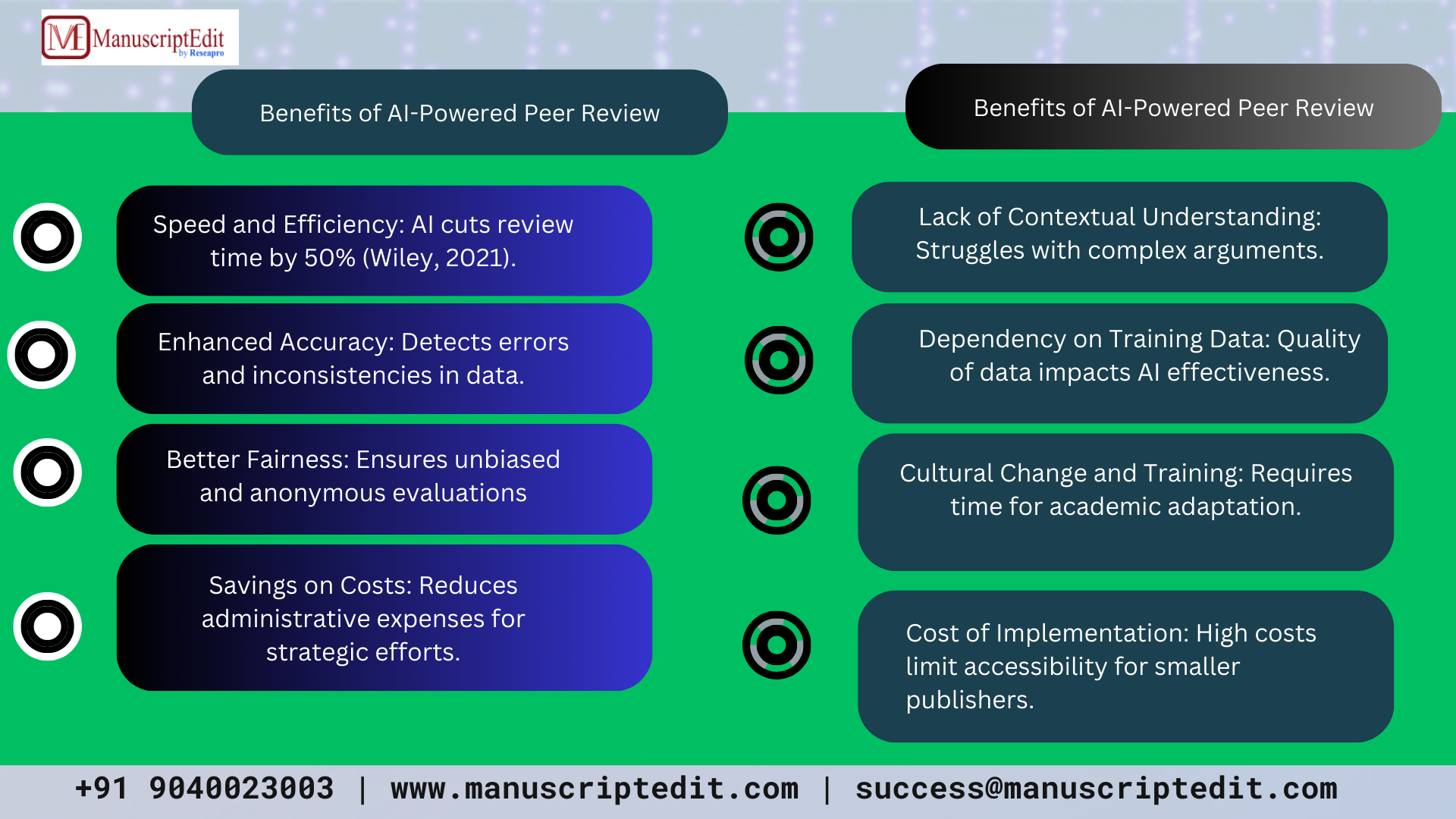
- Speed and Efficiency
AI tools make repetitive tasks easier, like finding reviewers and checking for plagiarism, leading to much faster review times. A study by Wiley (2021) showed that journals using AI reduced their average review time by half.
- Enhanced Accuracy
AI can look at large sets of data to ensure a thorough review process. For example, AI tools can find small differences in data or methods that human reviewers might miss.
- Better Fairness
AI makes the evaluations anonymous and consistent, hence giving equal opportunities to all authors irrespective of their backgrounds or connections.
- Savings on Costs
Automating tasks that take a lot of work reduces costs for administration. This lets resources be used for important efforts like training editors or reaching out to journals.
- Better Author Experience
AI tools also make things better for authors by giving them clear and helpful feedback. This advice helps authors improve their submissions and increases their chances of being accepted.
Limitations of AI in Peer Review
Though AI is promising, there are also problems:
- Lack of proper contextual understanding; AI might get the point wrong in complex arguments or innovative methods, resulting in incorrect appraisals.
- Dependency on the training data: The effectiveness of AI tools heavily depends on the quality and diversity of the data they were trained on. Bias can arise when there is not enough representation in the training data.
- Ethical considerations: Overreliance on AI may question the accountability and transparency of the decisions made.
- Cultural Change and Training: AI tools are a cultural change that requires academic institutions to change their way of teaching and learning. This process takes time.
- Cost of Implementation: The high-quality AI tools are very expensive, which makes them inaccessible to smaller publishers or institutions.
User Queries Answered
- How is AI being used to improve the peer review process?
AI is making the peer review process better by detecting plagiarism, selecting the best reviewers, offering detailed feedback on manuscripts, and helping to reduce bias through anonymous evaluations.
- What are the benefits of AI-powered tools in peer review?
These handy tools boost efficiency, accuracy, and fairness, while also lowering costs and easing administrative headaches. Plus, they support quicker decision-making and enhance the quality of publications.
- Can AI help detect plagiarism or ethical issues in submitted manuscripts?
Absolutely! AI tools like iThenticate and CrossRef can spot plagiarism and ethical violations with over 95% accuracy, which helps ensure the research we publish is credible.
- How does AI ensure transparency and fairness in peer review?
By keeping submissions anonymous and utilizing objective scoring systems, AI works to minimize human bias and create a fairer evaluation process.
- What are the limitations of using AI in peer review?
It’s important to note that AI has some limitations, including a lack of contextual understanding, dependence on the data it’s trained on, ethical considerations, and a reluctance to adopt new methods.
AI is truly revolutionizing the peer review process and is addressing long-standing concerns with bias, inefficiency, and ethical concerns. Innovative plagiarism detection tools, automated reviewer selection, and unbiased feedback are making academic publishing swifter, fairer, and more transparent. However, several issues still need to be addressed, and the inclusion of AI brings them tremendous potential in the future of research. So step into the future of peer review. Discover Manuscriptedit here to learn all about AI-based tools that can shift your publishing experience in the present.



