 Sci-Hub website has revolutionized scientific research by providing open access to millions of papers. This post delves into the mechanics of Sci-Hub’s database, exploring how it works and its significance in making scientific knowledge accessible to all, bypassing paywalls and copyright restrictions.
Sci-Hub website has revolutionized scientific research by providing open access to millions of papers. This post delves into the mechanics of Sci-Hub’s database, exploring how it works and its significance in making scientific knowledge accessible to all, bypassing paywalls and copyright restrictions.
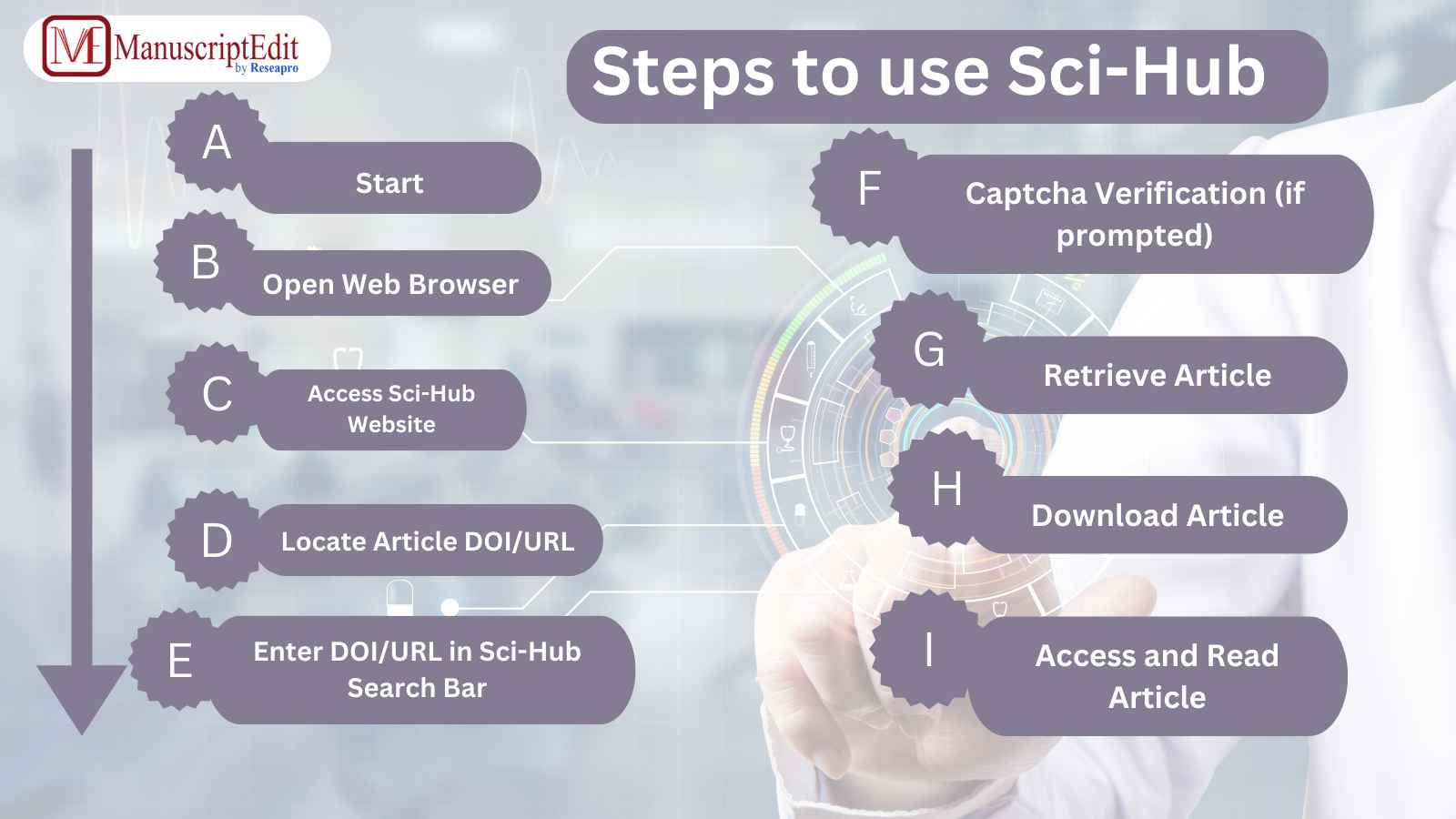
How to Use Sci-Hub?
 Sci-Hub’s database is a vast repository of scientific papers organized by metadata such as author, title, and (DOI) Digital Object Identifier which is a string of numbers, letters and symbols used to uniquely identify an article or document, and to provide it with a permanent web address (URL). Papers are added through user requests, crawling of online repositories, and donations from authors and publishers.
Sci-Hub’s database is a vast repository of scientific papers organized by metadata such as author, title, and (DOI) Digital Object Identifier which is a string of numbers, letters and symbols used to uniquely identify an article or document, and to provide it with a permanent web address (URL). Papers are added through user requests, crawling of online repositories, and donations from authors and publishers.

APIs facilitate data exchange and retrieval, while metadata enables efficient searching and filtering. The database is structured to allow for rapid access and downloading of papers, making scientific knowledge accessible to all.
 Data Retrieval and Access
Data Retrieval and Access
Through the Sci-Hub database, users can find publications by providing a DOI, sci-hub search for authors, or using keywords. They utilize a network of proxy servers, that can obtain papers from several sources while avoiding paywalls.
This procedure guarantees the timely and secure transmission of documents, enabling users worldwide to access scientific knowledge.
Database Maintenance and Updates
Sci-Hub’s database is maintained through regular crawls of online repositories, user submissions, and automatic quality control procedures. Errors are found and fixed via algorithmic checks and user feedback, while duplicate articles are found and eliminated.
This guarantees that the database is accurate, complete, and up to date, giving consumers dependable access to scientific knowledge.
Technical Challenges and Solutions
Sci-Hub faces technical challenges such as scaling to handle high traffic, ensuring security against cyber threats, and maintaining uptime despite legal pressures. To address these, Sci-Hub employs a distributed architecture, encrypts data and communications, and utilizes mirror sites and backup systems.
Additionally, the platform relies on a community-driven approach, with developers and users contributing to its maintenance and improvement.
Comparison with Other Open Access Initiatives
In terms of methodology and reach, Sci-Hub is distinct from other open-access projects such as arXiv, DOAJ, and Open Access Library. These platforms concentrate on hosting and disseminating preprints, post-prints, or certain topics; in contrast, Sci-Hub gathers and makes a wide range of published research publications accessible, frequently eluding paywalls.
It stands out due to its extensive database and intuitive layout, which make it a preferred resource for researchers worldwide. But what sets Sci-Hub apart from more conventional open-access venues are its contentious business practices and legal troubles.
Conclusion
To sum up, Sci-Hub’s database is powered by a sophisticated system of crawls, user uploads, and quality control. Sci-Hub has democratized access to scientific knowledge despite technological difficulties, promoting international research collaboration and advancement.
It significantly impacts closing the knowledge gap and advancing science for the good of humanity.
References
- https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA577512655&sid=googleScholar&v=2.1&it=r&linkaccess=abs&issn=13866710&p=IFME&sw=w
- https://www.academia.edu/71337197/Sci_Hub_a_challenge_for_academic_and_research_libraries?hb-sb-sw=81278617
- https://blogs.library.duke.edu/scholcomm/2016/03/03/some-radical-thoughts-about-scihub/